Tooth anatomy chart
Baby Teeth
The child's mouth contains 20 temporary teeth, called primary teeth, baby teeth, or deciduous teeth, consisting of the following teeth types:
4 second molars
4 first molars
4 cuspids (also called canine or eye teeth)
4 lateral incisors
4 central incisors
For each set of four teeth, two teeth are located in the upper arch (one on each side of the mouth) and two are located in the lower arch (one on each side of the mouth).
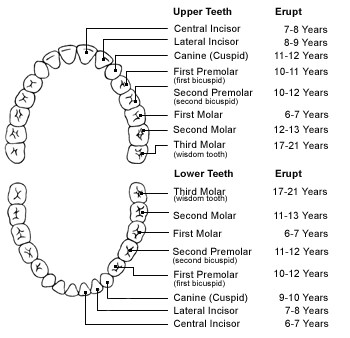
Permanent Teeth
The adult mouth contains 32 permanent teeth, consisting of the following teeth types:
4 third molars (also called wisdom teeth)
4 second molars (also called 12-year molars)
4 first molars (also called 6-year molars)
4 second bicuspids (also called second premolars)
4 first bicuspids (also called first premolars)
4 cuspids (also called canine or eye teeth)
4 lateral incisors
4 central incisors
Teeth Functions
Biting and tearing. The central incisors and lateral incisors are primarily used for biting and cutting and canine teeth are primarily used for tearing food.
Grinding and crushing. The premolars, molars, and wisdom teeth are primarily used for chewing and grinding food.
Internal Structure of Teeth
Each tooth consists of three main parts – the crown, the neck and root.
The crown is the visible part of the tooth; it is the portion that lies above the gum tissue. A protective layer called enamel covers the crown.
The neck is the area of the tooth between the crown and the root.
The root is the portion of the tooth that extends through the gum and into the bone of the jaw.









